IN THIS ARTICLE
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
“Real-time functionality” is rapidly becoming a requirement for software projects across many industries. What is “real-time”, and what’s driving this trend? Unlike typical “request/response” apps, where users have to reload a page, or press a button to get updates, real-time apps use the power of an always-on connection to receive data “as it happens.” Early real-time apps, like WebEx, Twitter, World of Warcraft, and Google Docs cost millions to build and scale. But these apps have also set the bar, and created the expectation for real-time. Real-time apps are infinitely more engaging.
Always-on, always-connected mobile devices are becoming ubiquitous, and users want to take advantage of their connectivity. And, the rapid emergence of the “Internet of Things” (aka IoT or M2M) trend is creating countless sources of real-time data streaming from connected devices all over the world. As users, we no longer want to wait for updates or a page to reload. Instead, we want to see information change “as it happens.” Take a taxi or ride sharing app for instance. You want to watch your cab as it approaches, on a map, in real-time.
And today, building real-time apps is easier, more accessible and cost effective than ever before. Realtime data stream networks are quickly establishing themselves as a key part of any next-generation software stack. These data stream networks serve the purpose of making it easier for developers to not only develop real-time applications, but deploy and scale them as well. Data stream network service providers (PubNub, Pusher, Firebase) offer the core building blocks needed to build and scale real-time apps.
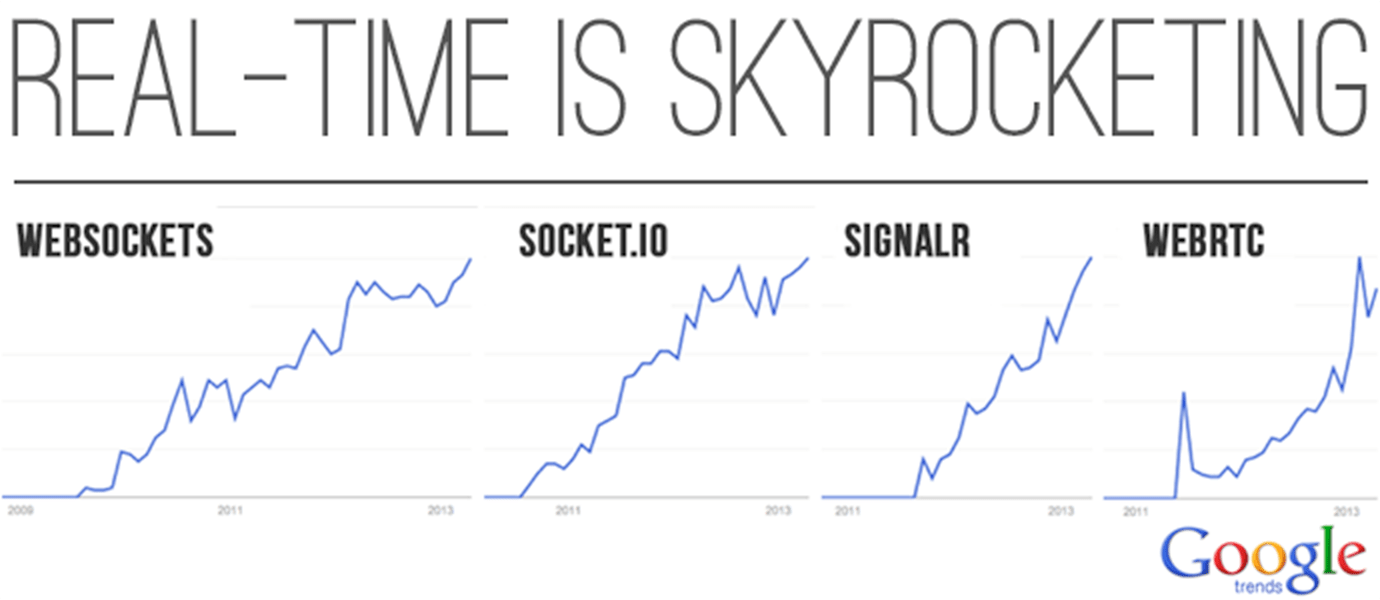
As a result, the demand for real-time is skyrocketing, and is showing no signs of slowing down.
Take a look at Google Trends for searches of popular real-time open source frameworks and protocols since 2009:
The Challenges of Real-Time
It’s clear that developers are looking for ways to deliver real-time solutions. Though while a myriad of protocols and open source tools can help with the development of real-time solutions, a majority of the challenge is in delivering and scaling real-time infrastructure:
- Conventional techniques for scaling traditional websites and app platforms is obsolete in the real-time world.
- Traditional web solutions for firewalls, load balancers, CDNs, monitoring tools, load testing, and redundancy strategies don’t work with socket-based real-time infrastructures.
- Real-world network conditions, like cell-tower hopping, NAT and firewalled environments, and even anti-virus software wreak havoc on home-grown real-time deployments.
- As your user base scales across the country or around the world, a globally distributed, redundant network of data centers is needed for maintaining that real-time experience for all users.
Solving these challenges is costly and time consuming. Even though an app works in the lab, it may not work in the real world.
The demand for reliable, scalable real-time applications have led to the emergence of data stream network service providers. A data stream network service provider takes care of the hassle up setting up, scaling, and maintaining a data stream network for you. As a result, data stream network service providers like PubNub have emerged, with strong VC backing and loyal, fast-growing customer bases.
The Real-Time Revolution
If you doubt the real-time revolution, just look at the apps you’ve got installed on your smartphone today. Real-time functionality has become intertwined an infinite amount of types of apps: from real-time taxi dispatch, to social TV, live voting and real-time charts and graphs. You can now chat in real-time within most social and business collaboration apps.

Real-time extends to many machine-to-machine use cases as well: apps now monitor and trigger irrigation equipment in real-time, new home automation systems are embedded with code that connects to data stream networks, and cars are embedding real-time to stream their telematics data to smartphones.
So what’s this mean for the future? Going forward, the core building-blocks found in data stream networks will become the standard way for apps to function and communicate. The old paradigms of request/response apps will fade, along with last-generation’s software stacks built around these models. With the rise in data stream networks, real-time is now easy and available for every developer, every app, and every organization in the world.