IN THIS ARTICLE
In our previous blog post, we showed you how to collect and publish realtime temperature and humidity data using the Tessel Climate module. Now it’s time to do something with that data.
In this blog post, we’re going to use the Tessel Climate module, AngularJS, the NVD3 library, and PubNub to graph realtime temperature and humidity data over a WiFi network.
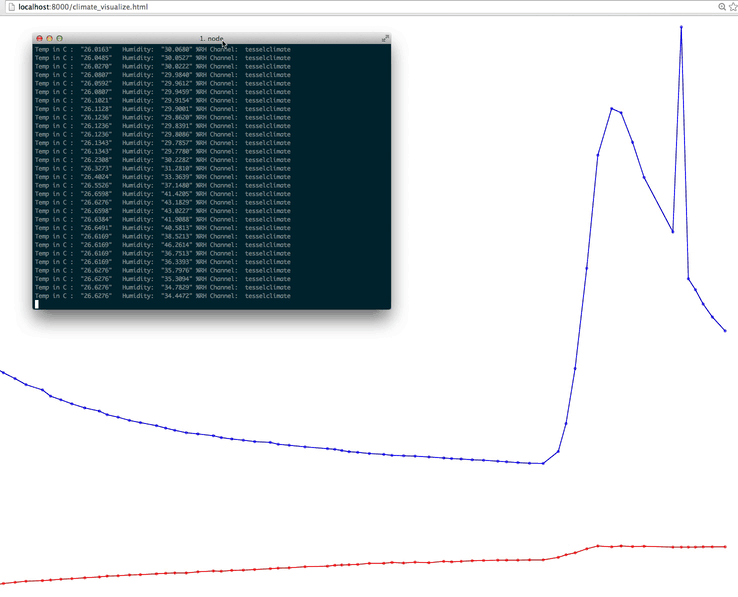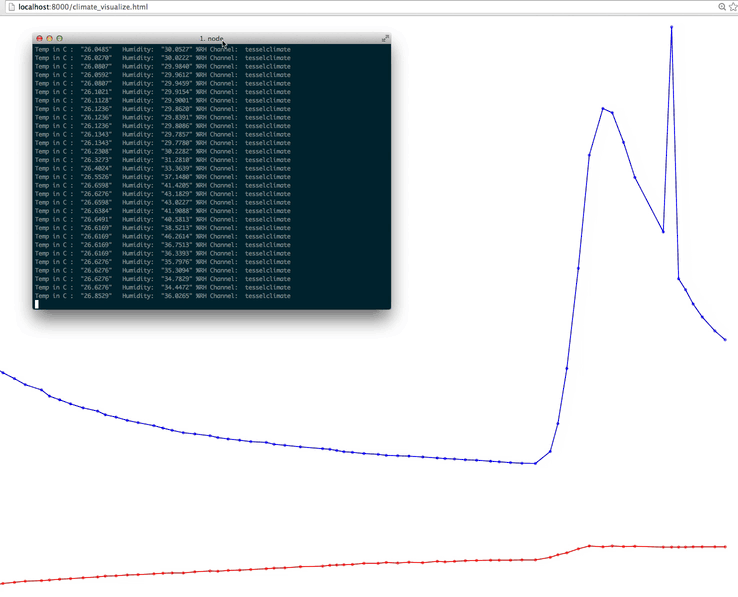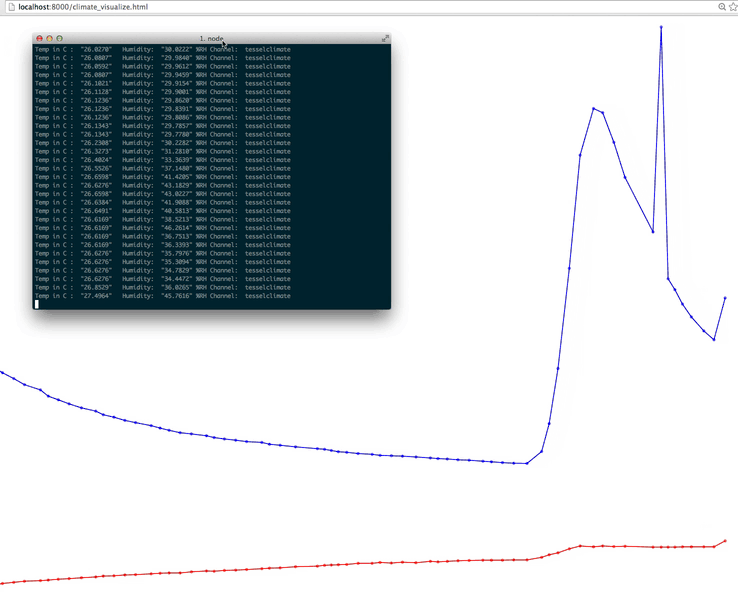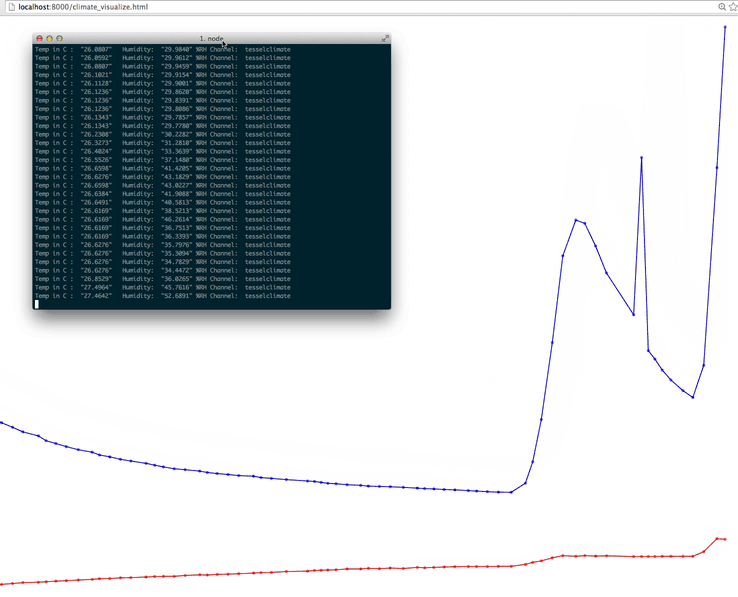
We’ll get something that looks like this:
This tutorial picks up where we left off in our last post. If you haven’t yet, start with part one, where we show you how to set up your module and start publishing data. Then come back to this point.
Displaying the Realtime Climate Data on a Graph
In an HTML file, we’ll create the view for the data.
First, we’ll have to include all of the special libraries to help us.
Include nvd3 CSS to style the graph:
Include the D3.js library:
Include nvd3:
Include the legend file from nvd3:
Include the line file from nvd3:
Include the utils file from nvd3:
Add scrolling to the body:
In the view, include the SVG we’ll be creating in the JavaScript.
Declare the Angular app and controller.
We’re all set up, now let’s get to the interesting part!
The Angular Magic
We’ll build a controller with the PubNub Angular dependency so we can listen to the PubNub channels.
We must subscribe to the same channel as our Tessel sensor is publishing. In this case, we’ve named it tesselclimate.
Next, we initialize the PubNub service. You’ll need your publish/subscribe keys, available in the PubNub Admin Dashboard.
The NVD3 will be expecting arrays of data that we can grab from the PubNub channel, so let’s set those up in preparation for receiving that data.
Finally, our Angular app can subscribe to the tesselclimate channel and register for new message events — the messages are the most recent climate data as the sensor reads it! So neat!
Each message will contain the data at the time the sensor takes the reading, temperature, and humidity.
We need to draw the graph, so we use NVD3 to assist us. In this case, we’re going to draw a line graph.
The addGraph function draws the graph with the data from the climateData function. For each data point taken, we gather the current time, temperature, and humidity. The x-coordinate for each temperature and humidity is the time when the corresponding climate reading is taken.
The y-coordinate is the temperature or humidity reading. In this way, we’re graphing two lines (temperature, humidity) vs. time. Feel free to change the colors of the lines!
With the Tessel already running, start a server locally and view the Angular file in your browser. Do you see a graph of temperature and humidity over time?
As you can see, our readings stayed pretty consistent. Try covering and uncovering the sensor and watch the graph change! You could really do a lot with this data, how would you use it?
Wrapping Up Tessel
In this blog post, we had fun showing you a how to graph realtime Tessel Climate module data with PubNub. We hope you find this information to be useful — it is really cool to see the Internet of Things grow!