IN THIS ARTICLE
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
The Internet of Things has found its way into our homes, cars, clothing, and much more, introducing new levels of convenience, interactivity, and monitoring. Beyond consumer and commercial applications, reliance on the Internet of Things has extended to the industrial sector.
The industrial IoT is data heavy and large scale. This goes beyond manufacturing and energy, and includes implementations with high data volume and mission critical applications. And one of the sectors at the forefront of industrial IoT is medical and healthcare.
A Massive Growing and Evolving Market
The healthcare market for the Internet of Things is estimated to hit $117 billion dollars by 2020. Why? Because the Internet of Things is being integrated into every cog of healthcare including:
- Patient monitoring and diagnostics
- Information and data transfer, storage, and collaboration
- Intelligent healthcare devices and tools (smart wheelchair, RFID, sensors)
- Connected emergency units, response vehicles, and hospitals
So with a massive reliance on the IoT in healthcare, how are we actually connecting these devices? What are the lines between the sensors, smart tools, patient records, applications, and the massive amounts of data that need to get from Point A to Point B?
The realtime data stream network.
A data stream network is basically a massive publish/subscribe network, globally redundant, that sends raw data bidirectionally between devices, users, and servers. Integrated in the Internet of Things, a data stream network is the messaging (or communication) layer that breathes life into the IoT and its billions of connected devices. With healthcare and IoT, where data transfer needs to be reliable and secure, a data stream network is imperative.
Realtime Technology in the Medical IoT
You may have noticed the internet-connected MRI, heart rate monitor, or other equipment at your last hospital visit, but how are these technologies affecting those who work closest with these devices and their beneficiaries?
Let take a look at how IoT mobile realtime communication apps are impacting the lives of nurses, physicians, administrators, as well as health care recipients. We’ll also look at healthcare IoT communication security, and how and why a data stream network needs to secure that data.
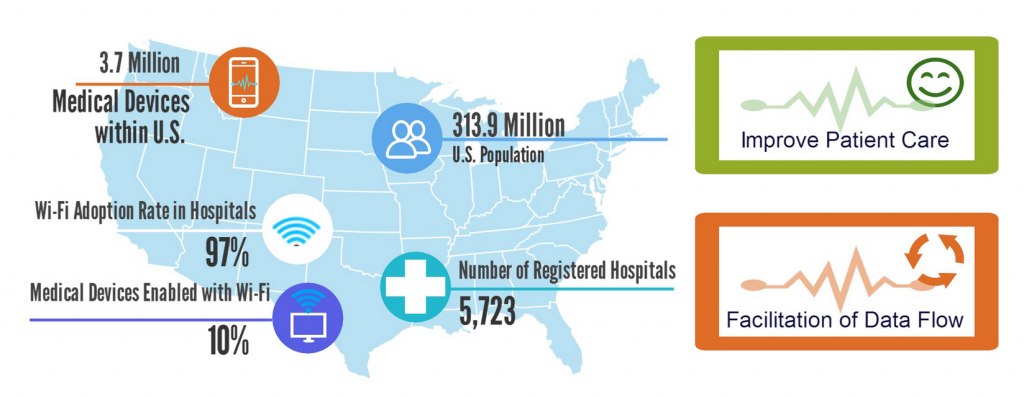
Source: https://www.lairdtech.com/solutions/embedded-wireless/what-connected-hospital/connected-hospital-infographic
Data Delivery and Synchronization
Medical IoT has evolved the quality of patient care through more reliable and efficient communications among caregivers. Using mobile applications and secure networks, nurses are able to instantly access patient information, and updates are synced in realtime across all other connected mediums. Readings and collected data from sensors are streamed, stored, or published in realtime, and their current status is synced.
This is essential for mission critical situations where both time and accuracy of data is of the utmost value. With mobile alert notifications, nurses and staff are able to achieve a new level of mobility and communication efficiency, keeping the team connected, informed and patient focused. Decreased response means healthy, happier patients, as well as improved benchmarks for responding to patients.
Geolocation and Presence
Mobility is a central feature of healthcare IoT. With emergency response units, the tracking of geolocation, as well as efficient dispatch of response teams could be a matter of life or death. Physicians are often required to move between patients, units, clinics, laboratories, operating rooms, and offices.
Mixing presence functionality with realtime mapping and geolocation, mobility can be tracked and coordinated and executed on.
Based on geo-proximity, physicians can also access patient information and patient’s care teams at any place and anytime through realtime chat or text messaging. Stronger accessibility to patients and patient’s care team means more accurate and expedient patient treatments and stronger collaboration between care teams.
Administration
When it comes to medical administration, quality, cost, and efficiency are of the highest priority. In the past, many hospital administrators faced the challenge of choosing between a digital and an analogue solution for clinical workflow. However, with IoT technology become more available and affordable, many administrators have already taken the leap.
Speedy message delivery and automatic audit trails eliminates the need for pagers and other wireless alternative which can often be bulky outdated. With realtime access to patient information staff can spend more time caring for patients while avoiding the risk miscommunication or data delays – both costly occurrences in a hospital.
With both patient specific and big data information, hospitals can more efficiently schedule patients by collecting and utilizing statistics in a cloud-based scheduling application. The result of this is faster turnover and more satisfied patients.
Technicians
Cloud-based data utilization is also proving to be useful for medical device technicians. With an internet connected device, not only can technicians know exactly where the problem is, but they can be notified immediately, potentially reducing device downtime. Additionally, the device, in coordination with the hospital’s patient scheduling system, can redirect patients to a location with an available device or reschedule patients.
Security and Confidentiality
When it comes to patient and medical data, confidentiality and security is paramount. When transferring and syncing information between connected devices, data must be encrypted from endpoint to endpoint. Authentication (two-factor preferably) should be built into IoT applications.
 Lastly, legislative security requirements and global regulations, most notably HIPAA for healthcare, are constantly evolving and need be be addressed and updated. In looking at securing the healthcare Internet of Things from a global regulations standpoint, design patterns need to be implemented to comply.
Lastly, legislative security requirements and global regulations, most notably HIPAA for healthcare, are constantly evolving and need be be addressed and updated. In looking at securing the healthcare Internet of Things from a global regulations standpoint, design patterns need to be implemented to comply.
For example, data routing to avoid specific areas. using a Data Stream Network, streams of data can be customized to be routed through specific regions, countries, etc. But this doesn’t just apply to the transferring of data, but also the storage of data, as well as retention requirements. All these compliances must be taken into account when it comes to the healthcare IoT.
To learn more about the security risks and challenges of IoT, including healthcare and global regulations, check out the great panel below from IoT StreamConf 2015:
Looking Forward
The Internet of Things and healthcare has a bright, but complex future. After all, it’s human health we’re talking about here. And the big question?
How can we harness the power of the Internet of Things to push healthcare forward?
One of the essential pieces is how we’re going to connect healthcare devices, systems, professionals, and networks in realtime, to reliably and securely stream data. And with a data stream network and a publish/subscribe design pattern, we can do just that.










